Two page worksheet using specific heat capacity. You will be quizzed on terms such as heat energy and kinetic energy.
 Specific Heat Worksheet Name Date Q Mct Whereq Heatenergy M Mass
Specific Heat Worksheet Name Date Q Mct Whereq Heatenergy M Mass 1000ml of 40 0c water is heated until its temperature is 37 0c.

Calculating specific heat worksheet answers. For q m c d t. Specific heat capacity handout answer key objectives calculate the specific heat capacity of a liquid. Determine the amount of energy required to heat a liquid to a particular temperature.
Identify each variables by name the units associated with it. Worksheet calculations involving specific heat 1. Identify each variables by name the units associated with it.
This quiz and worksheet gauge your knowledge of specific heat capacity and how it is calculated. For q m c d t. If the specific heat of water is 418 jg 0c calculate the amount of heat energy needed to cause this rise in temperature.
Specific heat capacity worksheets showing all 8 printables. Calculate the heat capacity of a piece of wood if 15000g of the wood absorbs 675 x 104 joules of heat and its temperature changes from 32 0c to 57 0c. Explain how they differ from each other.
Heat is not the same as temperature yet they are related. Q amount of heat j m mass grams c specific heat jg0c dt change in temperature 0c. Answers included on separate sheet.
Data collection answers will vary depending on collected data. Heat and heat calculations key name 1. Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy and does not depend upon the amount of matter in the sample.
Worksheet calculations involving specific heat 1. About this quiz worksheet. Worksheets are name per work introduction to specific heat capacities specific heat latent heat and.
Also includes a spreadsheet to show how the calculations have been done. J ri phufxu lv khdwhg iurp wr dqg devruev mrxohv ri khdw lq wkh surfhvv dofxodwh wkh vshflilf khdw fdsdflw ri phufxu kdw lv wkh vshflilf khdw fdsdflw ri vloyhu phwdo li j ri wkh phwdo devruev ri khdw. Questions start easy then become gradually harder.
Example answers in table below. What is the difference in temperature and heat.
 What Is Joule Heating Producing Heat With Electric Current
What Is Joule Heating Producing Heat With Electric Current  Ees Engineering Equation Solver F Chart Software Engineering
Ees Engineering Equation Solver F Chart Software Engineering 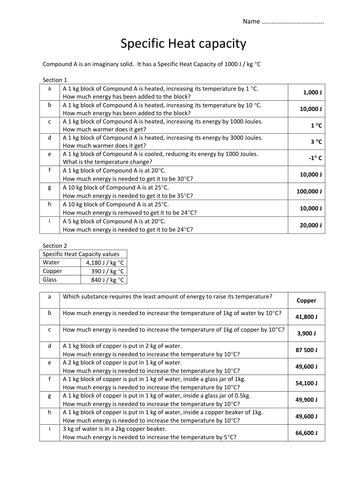 Specific Heat Capacity Worksheet With Answers
Specific Heat Capacity Worksheet With Answers  The Enthalpy Of Neutralization Of Phosphoric Acid Worksheet Ch 222
The Enthalpy Of Neutralization Of Phosphoric Acid Worksheet Ch 222  How To Read Manual J Load Calculation Reports Energy Vanguard
How To Read Manual J Load Calculation Reports Energy Vanguard  Le Chatelier S Principle Chemical Equilibrium Siyavula
Le Chatelier S Principle Chemical Equilibrium Siyavula  Superheated Steam
Superheated Steam  Measuring The Quantity Of Heat
Measuring The Quantity Of Heat  Ncert Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 12 Thermodynamics
Ncert Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 12 Thermodynamics 

0 comments